KÖCO Stud Types
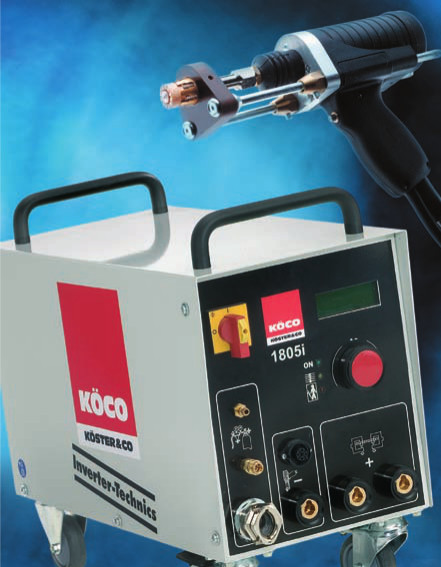

Introduction
KÖCO stud welding is a safe high-performance fastening technology offering the users an enormous potential for cost reduction. With KÖCO stud welding technology threaded and unthreaded studs, shear connectors, refractory anchors, etc. with diameters ranging from 2 to 25 mm, are joined to metal sheets, pipes, profiles, etc. by instantaneous cross-sectional welding. Some costly and time-consuming operations, such as drilling, threading, screwing or manual welding, are no longer necessary.
The advantages of KÖCO stud welding technology are obvious:
- A high degree of safety, thanks to cross-sectional joints
- High productivity through extremely short welding time
- Options for various combinations of materials
- Distortion reduced to a minimum through low thermal stress
- Very little or no damage to the reverse side
- Hollow parts remain leakproof
- Access to parts from one side only is sufficient
- Easy to operate for personnel trained on the job
- Conform to international standards: EN ISO 14555 and EN ISO 13918
- Shear connectors officially approved: European Technical Approval ETA-03/0039
- Innovative stud welding equipment and welding studs from in-house production


Users of KÖCO-Stud Welding
KOCO stud welding technology is suitable for applications in:
- Composite structures of steel and concrete: brigde building, high rise buildings, industrial buildings, multi-storey car parks, prefabricated structures, foundation work and tunnelling, hydraulic steel work
- Steel construction: mounting of facades, pillars, rails
- Shipbuilding: assembly devices, insulations, cable tracks and fastening of equipment, anti-skid flooring on ramps, production of manhole rings, etc.
- Construction of containers and machinery: boilers, chemical laboratory equipment, tanks, ventilation and air conditioning technology, switchboards, billboards, food industry, domestic applicances.
- Vehicle construction: fastening of cables and leads, decorative borders, earthing studs, linings, etc.
- Refractory industry: fastening of fire-proof concrete, ceramic linings, fibre mats in kilns, boilers, waste incinerators, etc.
- Production and processing of raw materials: anti-wear studs, spikes, mounting of hard facings.

Technology of Stud Welding
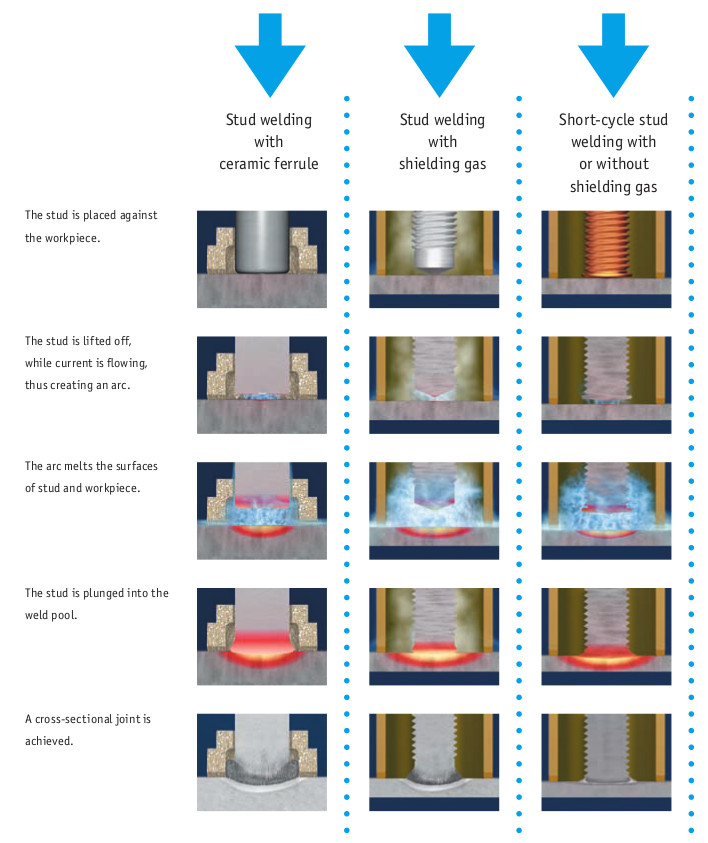
In drawn arc stud welding, an arc is drawn between a stud and a workpiece, melting some of the metal on both parts. At the end of welding time the stud is plunged into the weld pool, the welding current is switched off and the weld pool solidifies.
Depending on the application, the following processes are available:

Drawn arc stud welding variants:
- stud welding with ceramic ferrule
- stud welding with shielding gas
- short-cycle stud welding with or without shielding gas
Stud welding with tip ignition variants:
- with gap
- with contact
Selection of the Process
| Process | Stud welding with ceramic ferrule | Stud welding with shielding gas | Short-cycle stud welding | Stud welding with tip ignition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
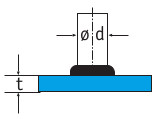
| Minimum sheet thickness t | 1/4 d | 1/8 d | 1/8 d | 1/10 d, min. 0.5mm |
| Maximum stud diameter d for welding from different positions | ↓ 25 ← 16 ↑ 20 |
↓ 12(16) ← 6 ↑ 8 |
↓ 12 ← 8 ↑ 10 |
↓ 8 ← 8 ↑ 8 |
| Suitable surface conditions ¹ | bright metal, rolling skin, primer suitable for welding, surface rust, thin layer of oil | bright metal, rolling skin, primer suitable for welding, surface rust, thin layer of oil, zinc coating | bright metal, rolling skin, surface rust, thin layer of oil, zinc coating | bright metal, thin layer of oil, galvanized (with a possible limit to the stud diameter) |
| Unsuitable surface conditions | hot-dip galvanizing, loose layers of scaling, heavily corroded, protective coating | loose layers of scaling, heavily corroded, protective coating | loose layers of scaling, heavily corroded, coating with organic material | zinc coating of more than 15 μm, coating with organic material, coating with insulating material (e.g. anodized aluminium) |
| Common applications | studs with more than 8mm ø in steel and boiler construction, and shipbuilding, on surfaces only coarsely cleaned, deep penetration, suitable for field welding | studs from M 6 to M 12 in downhand position, especially with automatic feeding of studs | studs from 5 to 10mm ø without shielding of the weld pool in case of average quality requirements for the shape of the weld collar. In case of high-grade requirements, shielding gas should be used. | for thin metal sheets, especially stainless steel and aluminium, and in case of high-grade requirements for an undamaged visible reverse side |
 ¹ Here, we can only give general hints without any commitment or warranty on our part. The conditions must be tested in each individual case. Basically, a higher degree of surface cleanliness is required for shorter welding times. The best results are always achieved on bright metal surfaces.
¹ Here, we can only give general hints without any commitment or warranty on our part. The conditions must be tested in each individual case. Basically, a higher degree of surface cleanliness is required for shorter welding times. The best results are always achieved on bright metal surfaces.
Common Stud / Workpiece Material Combinations in Drawn Arc Stud Welding
| Stud material | Workpiece material | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| low-alloy steel with a minimum yield point of ≤ 460 N/mm² | thermo-mechanically treated and annealed with fine-grain steel with a minimum yield point > 460N/mm² | austenitic stainless steel and Duplex steel | pure aluminium and non-hardenable aluminium alloys | |
| low-alloy steel, e.g.S235, 4.8(suitable for welding), 16Mo3 | a | b | b ² | - |
| heat-resisting ferritic and austenitic steel, e.g. 1.4301, 1.4571 | c | c | c | - |
| austenitic stainless steel, e.g. 1.4301, 1.4571 | b/a ¹ | b | a | - |
| aluminium-magnesium alloys, e.g. AlMg3, AlMg5 | - | - | - | b ³ |
|
¹ upto 10mm ø and with shielding gas ² only short-cycle drawn arc stud welding ³ for stud diameters up to 10mm only |
- unsuitable for welding a suitable for any application including force transfer b limited suitability for force transfer c generally suitable, limited suitabiity, for heat transfer only |
Common Stud / Workpiece Material Combinations in Stud Welding with Tip Ignition
| Stud material | Workpiece material | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| low-alloy steel, fine-grain steel, annealed steel C ≤ 0.35% | low-alloy steel, fine-grain steel, annealed steel C ≤ 0.35%, zinc- or metal-coated, thickness of coating ≤ 15 μm | austenitic stainless steel | pure copper and unleaded copper alloys | pure aluminium and non-hardenable aluminium alloys | |
| low-alloy steel, e.g.S235, 4.8(suitable for welding) | a | b | a | b | - |
| austenitic stainless steel, e.g. 1.4301 | a | b | a | b | - |
| brass (unleaded) | b | b | b | b | - |
| Al99,5 | - | - | - | - | b |
| AlMg3 | - | - | - | - | a |
- unsuitable for welding
a suitable for any application including force transfer
b limited suitability for force transfer

 Surecon Fastening
Surecon Fastening Welding Machines
Welding Machines Köco Stud Welding
Köco Stud Welding













